Treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Lipoprotein apheresis
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a common inherited cause of premature cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. This genetic disorder is characterized by high to extremely high blood levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c or "bad cholesterol").
Lipoprotein apheresis can be a treatment of choice for those homozygous, and second-line for heterozygous hypercholesterolemic and hyper-Lp(a) patients, when conventional pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments for dealing with elevated lipid blood levels prove inadequate or are not sufficient to achieve desired lowering of low‑density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) and lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)).1
In lipoprotein apheresis, a distinction is made between whole-blood treatment and the plasma method. Fresenius Medical Care offers an adsorption system for whole-blood treatment (DALI Adsorbers) and a filtration system for the plasma method (MONET Plasma Fractionator).
DALI Adsorbers

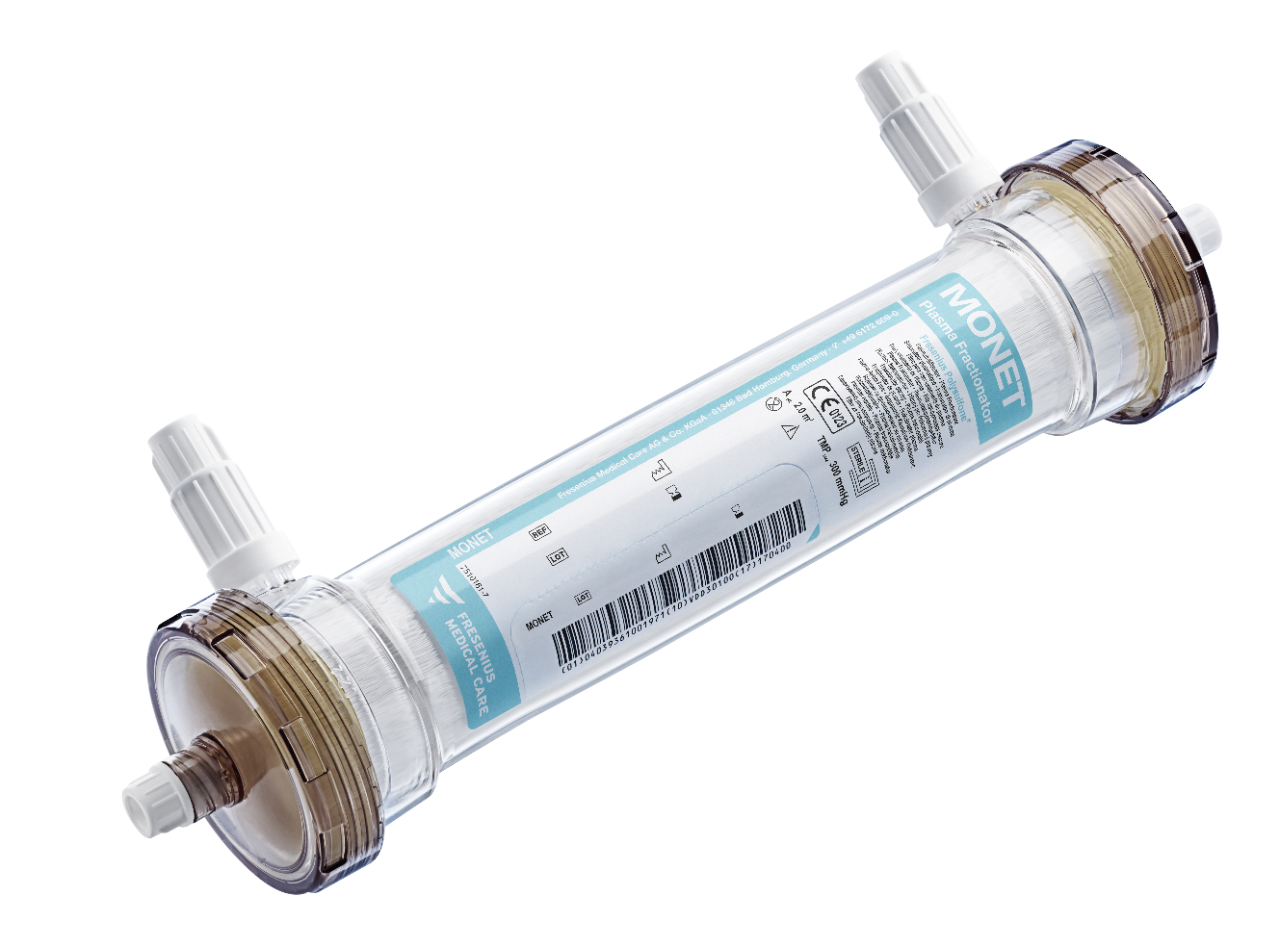
MONET Plasma Fractionator

DALI Adsorbers*
Semi-selective lipoprotein adsorption
DALI lipoprotein apheresis is used to treat patients with severe hypercholesterolemia and/or elevated levels of lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)). The objective is to reduce levels of LDL-c and Lp(a). This is an effective approach to reduce MACE (major adverse coronary events) in patients on very high cardiovascular risk.2,3
Lipoproteins such as LDL or Lp(a) are largely removed by electrostatic interactions between the positively charged apolipoprotein and the negatively charged adsorber material.4 The reduction of LDL-c and Lp(a) levels can be individually adapted to a patient’s therapy needs by means of different adsorber sizes (DALI 500 Adsorber and DALI 750 Adsorber) and configurations of these (DALI 1000 and DALI 1250).5,6
During a single treatment, the levels of LDL-c and Lp(a) were reduced by a mean of 71% and 64%, respectively.8
MONET Plasma Fractionator
Filter for effective reduction of high molecular weight proteins
The MONET Plasma Fractionator is indicated for use in therapeutic apheresis, to reduce high molecular plasma constituents such as Lp(a), LDL-c, fibrinogen and immunoglobulin M (IgM) (e.g. in order to reduce LDL-c and Lp(a) in patients with hyperlipoproteinemia).7,8,10
LDL-c, Lp(a) and fibrinogen are removed from plasma by filtration: The target plasma constituents are retained by the fine pores of a plasma fractionating membrane, whereas smaller plasma constituents, such as HDL or albumin, pass the pores and return to the patient.7,8,10
The MONET Plasma Fractionator contains a Fresenius Medical Care polysulfone membrane, based on Fresenius Medical Care membrane technology and enhanced for use in lipoprotein filtration.10
Related content
1 Padmanabhan A et al. J Clin Apher 2019; 34:171-354
2 Schettler et al. Clin Res Cardiol Suppl 2017; 12:44-49
3 Schettler et al. Clin Res Cardiol Suppl 2019; 14:33-38
4 Bosch Ther Apher 2001; 5(4):239-243
5 Bosch et al. Ther Apher Dial 2006; 10(3):210-218
6 Dräger et al. Eur J Clin lnvest 1998; 28:994-1002
7 Kozik-Jaromin et al. Atheroscler Suppl 2017;30:225–231
8 Ramlow et al. Atheroscler Suppl 2017; 30:217-224
9 Raina et al. Blood Purif 2019; 47(4):301-316
10 Instructions for Use MONET Plasma Fractionator (7510181 02/21)
11 Julius et al. Ther Apher Dial 2013; 17(2):179-184
12 Julius et al. Atheroscler Suppl 2015; 18:95-102
13 Padmanabhan A et al. J Clin Apher 2019; 34:171-354; PVD see pages 281-282
14 Mehdi M et al.; Nephrol Dial Transplant 2019; 34(S1):i234-i235
15 Pithova P et al. Poster presented at the DFSG congress; 2017 Sept 8 -10; Porto, Portugal
16 Soltész P et al. Orv Hetil 2021; 162(10):375-382